Anti platelet drugs prevent platelet aggregation. They are also known as anti thrombotic drugs as they prevent the formation of platelet rich thrombus. They increase the bleeding time.
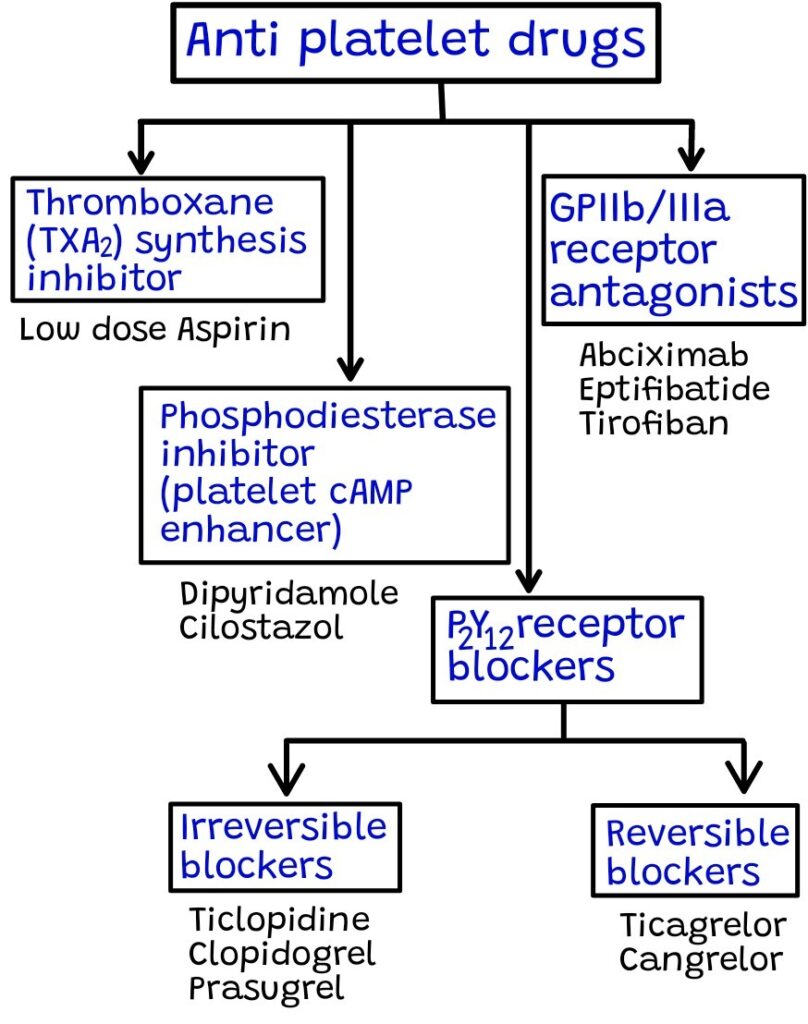
Classification:
Mechanism of action:
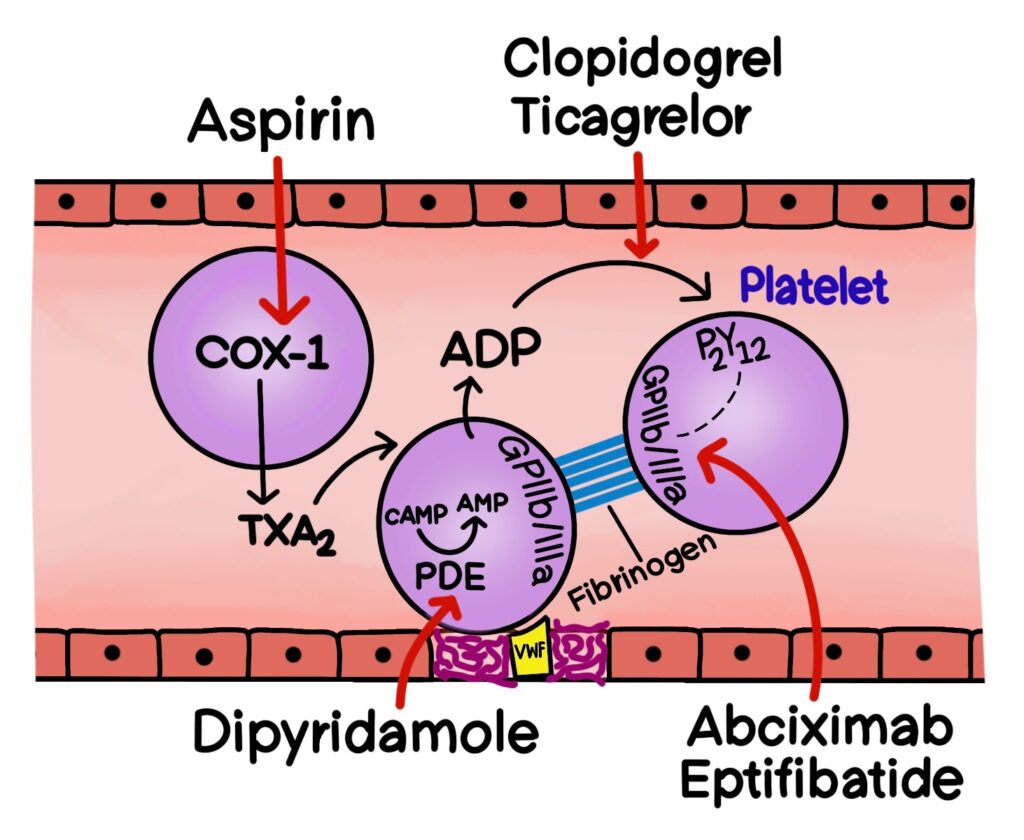
- Thromboxane (TXA2) synthesis inhibitor: Low dose aspirin irreversibly inhibits the COX-1 enzyme present in the platelet. This leads to reduced production of TXA2 and inhibits platelet attachment. Platelets lacking a nucleus cannot synthesize new enzymes, so the anti platelet effect lasts for the lifespan of the platelet, which is 7 to 10 days. For this reason aspirin should be stopped 7 days prior to surgery.
- Phosphodiesterase inhibitor: Dipyridamole inhibits phosphodiesterase 3 (PDE 3) enzyme which is responsible for the breakdown of cyclic Adenosine Monophosphate (cAMP) into AMP. So by blocking this enzyme, intracellular levels of cAMP increases and ultimately inhibits platelet recruitment.
- P2Y12 receptor antagonists: Ticlopidine, clopidogrel and prasugrel are prodrugs and they irreversibly blocks the purinergic (P2Y12) receptors present on the surface of the platelets. On the other hand, ticagrelor and cangrelor are active drugs and they reversibly blocks the P2Y12 receptors. This they inhibit ADP mediated platelet aggregation.
- GPIIb/IIIa inhibitors: Abciximab, eptifibatide and tirofiban act by inhibiting the GPIIb/IIIa receptos present on the surface of the platelets. Fibrinogen normally crosslinks these receptors leading to platelet aggregation. Therefore, inhibiton of these receptors prevents platelet aggregation. These drugs are administered IV.
Uses:
- Aspirin is the drug of choice for MI and stroke.
- Aspirin 75-100mg/day oral should be given life long to post-MI patients as it decreases the recurrence of MI or stroke. It is also used as prophylaxis for Coronary Artery Disease (CAD).
- Aspirin in combination with other anti platelet drugs is used as Dual Anti Platelet Therapy [DAPT]. Example- Aspirin in combination with clopidogrel is given in acute coronary syndrome, which includes unstable angina, NSTEMI and STEMI.
- Ticlopidine is given for prevention of stroke in patients with a history of Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA).
- Cilostazol is used in the treatment of intermittent claudication.
- Dipyridamole in combination with warfarin is used for primary prophylaxis of thromboemboli in patients with prosthetic heart valves.
Adverse effects:
- The most important adverse effect of all anti platelet drugs is bleeding.
- Longterm use of aspirin may cause peptic Ulcers.
- P2Y12 receptor blockers produce adverse effects like nausea, diarrhea and Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia Purpura (TTP).
- Ticlopidine is rarely used because it causes bone marrow suppression and leads to agranulocytosis.
- Dipyridamole causes headache and hypotension due to its vasodilation properties.
Contraindications: Aspirin should not be given during lactation as it causes Reyes syndrome. Anti platelet drugs are contraindicated in patients with bleeding disorders, as they can cause severe bleeding.
Drug-Drug interactions: The prodrug clopidogrel requires CYP2C19 enzyme for its activation. Omeprazole, which is a proton pump inhibitor given for peptic ulcer inhibits CYP2C19. So, clopidogrel cannot be converted to its active form. Hence, omeprazole should be avoided with clopidogrel.