Giardia Lamblia also known as Giardia intestinalis or Giardia duodenalis is an intestinal flagellate protozoan. It causes ‘Giardiasis’. The two morphological forms of Giardia Lamblia are cyst and trophozoite.
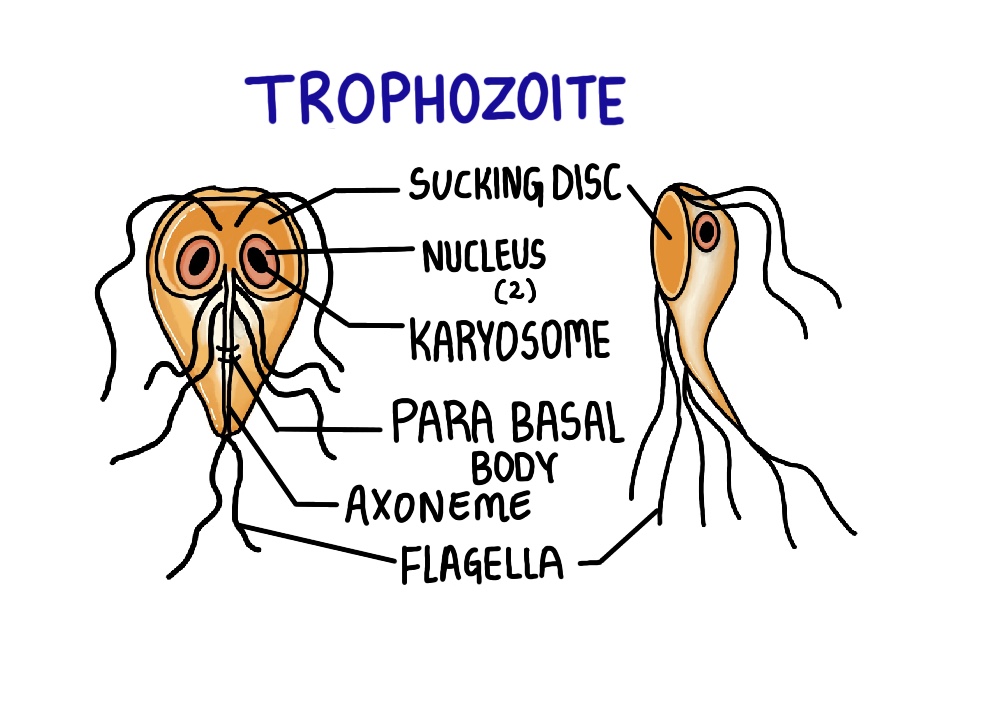
Trophozoite:
In the front view, the trophozoite is pear-shaped and in the lateral view, it is teardrop or spoon shaped. It has 2 nuclei with small karyosomes and 4 pairs of flagella. These flagella act as organs of locomotion and show falling leaf motility. The trophozoite also has an axoneme, a parabasal body, and a sucking disc. It is the pathogenic, feeding and replicating form.
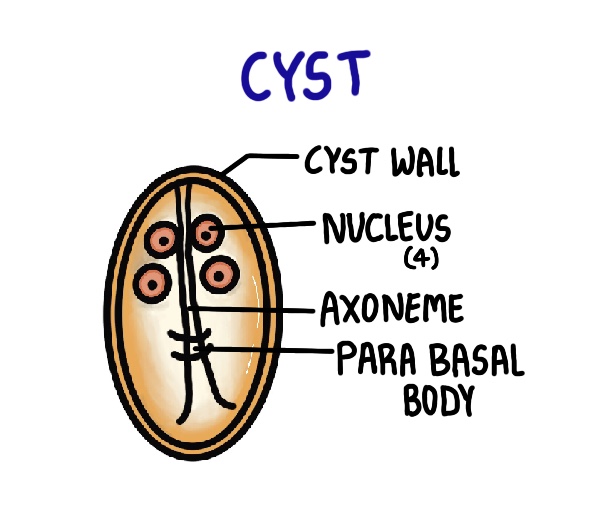
Cyst:
The cyst is oval shaped with 4 nuclei. It has an axoneme, a parabasal body and a cyst wall. The cyst is smaller than the trophozoite and is the infective form.
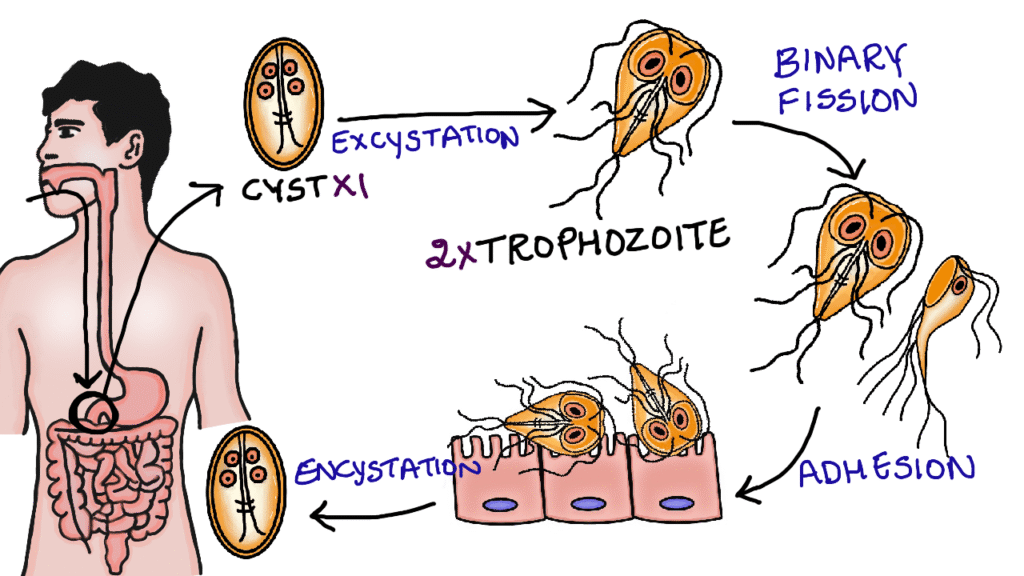
Life cycle:
Man acquires infection by ingestion of food contaminated with infective cysts. After ingestion, these cysts are carried to the duodenum. Here they undergo excystation and transform into trophozoites. Each cyst gives rise to two trophozoites. The trophozoites undergoes asexual reproduction through longitudinal binary fission.With the help of sucking disc, the trophozoites adhere to the duodenal mucosa.In the active stage of the disease, the trophozoites are seen in the stool as they are directly excreted. The trophozoites then moves to the jejunum, where they undergo excystation to form the cysts. The cysts are then excreted in the feces. Although, both cysts and trophozoites can be excreted in the feces, only cysts are capable of surving outside the host.
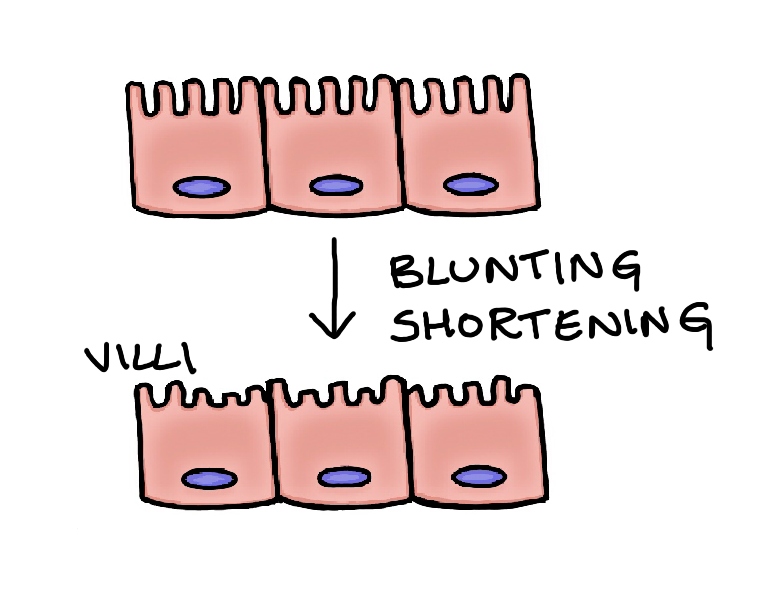
Pathogenesis:
Giardia Lamblia causes blunting and shortening of the intestinal villi, leading to malabsorption of fat, vitamin A, vitamin B12 and iron. Damage to the brush border causes deficiency of disaccharidase enzymes, resulting in lactose intolerance.
Clinical features:
Most of the infected individuals are asymptomatic carriers .Steatorrea or non bloody diarrhea is seen in Giardiasis due to malabsorption of fat. It is characterized by pale, bulky, foul smelling stools that are difficult to flush. Other symptoms include abdominal pain, bloating, vomiting and weight loss.
Diagnosis:
Stool microscopy: In stool microscopy, both cysts and trophozoites can be seen and are identified based on their characteristic morphology.
String test: In the string test, a gelatin capsule containing a thread is swallowed. It goes to the duodenum and gets dissolved. After some time, the string is pulled out and the duodenal contents are examined under a microscope.
Other diagnostic methods include duodenal biopsy, antigen detection and PCR.
Treatment:
Tinidazole or metronidazole is used in the treatment of Giardiasis.