It is a chromosomal disorder arising due to trisomy 21. A normal human cell contains 46 chromosomes that are arranged in pairs. In down syndrome there is an extra copy of chromosome 21. Out of these three copies, mostly two copies are contributed by the mother and one copy is from the father. One of the major risk factors for down syndrome is maternal age. Its incidence is 1 in 700 newborns. About 95% of down syndrome cases are caused due to meiotic nondisjunction and 4% are due to Robertsonian translocation.

Meiotic nondisjunction:
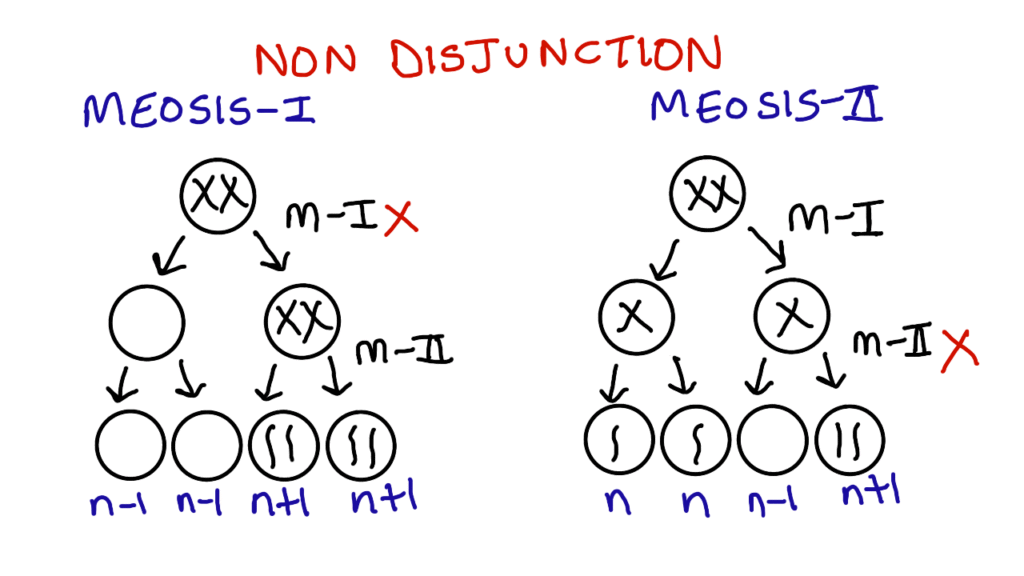
In normal meiosis-1, the homologous chromosomes separate into two cells. The sister chromatids of the chromosomes of these cells further divide in meiosis-2, forming four gametes each with the single chromosome copy, that is n. The nondisjunction causing trisomy 21 can occur either in meiosis-1 or meiosis-2.
If nondisjunction occurs in meiosis-1, the homologous chromosomes fail to separate. This results in one cell with an extra chromosome and the other cell with none. After meiosis-2 the gametes formed from the cell with the extra chromosome have an additional copy(n+1), while the gametes formed from the other cell have no copy(n-1).
If nondisjunction occurs in meiosis-2, meiosis-1 will proceed normally. For example if the defect occurs in the right cell it produces abnormal gametes (n-1) and (n+1), while the other cell produces two normal gametes(n). This n+1 gamete, when fused with a normal sperm(n) results in the formation of 2n + 1 that is trisomy. The karyotype in this condition is 47 x x + 21 or 47 xy + 21.
Robertsonian translocation:
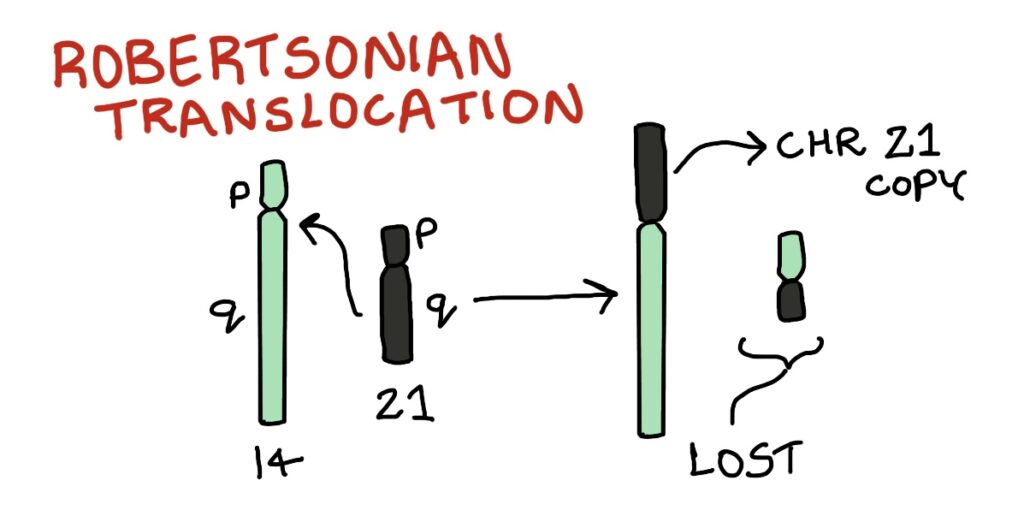
In robertsonian translocation, the long arm(q) of chromosome 21 is translocated to the long arm of chromosome 14. The small chromosome made up of the short arms(p) of chromosome 21 and 14 is lost due to its small size. This fused chromosome(14q;21q) carries all the information of chromosome 21. We know that a gamete contains 23 chromosomes and if a mother who is a carrier of robertsonian translocation produces a gamete. There are chances that out of these 23 chromosomes there will be one normal 21 chromosome and one fused or translocated chromosome. This fused chromosome behaves as a copy of chromosome 21. Fertilization with the sperm adds another normal chromosome 21. So, in individuals with down syndrome due to robertsonian translocation there are 46 chromosomes but still have three copies of chromosome 21, unlike the 47 chromosomes seen in case of non disjunction.
Clinical features
1.Intellectual disability
2.Congenital heart diseases like atrioventricular septal defects
3.Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia(ALL) or Acute Myeloid Leukemia(AML)
4.Alzheimer’s disease
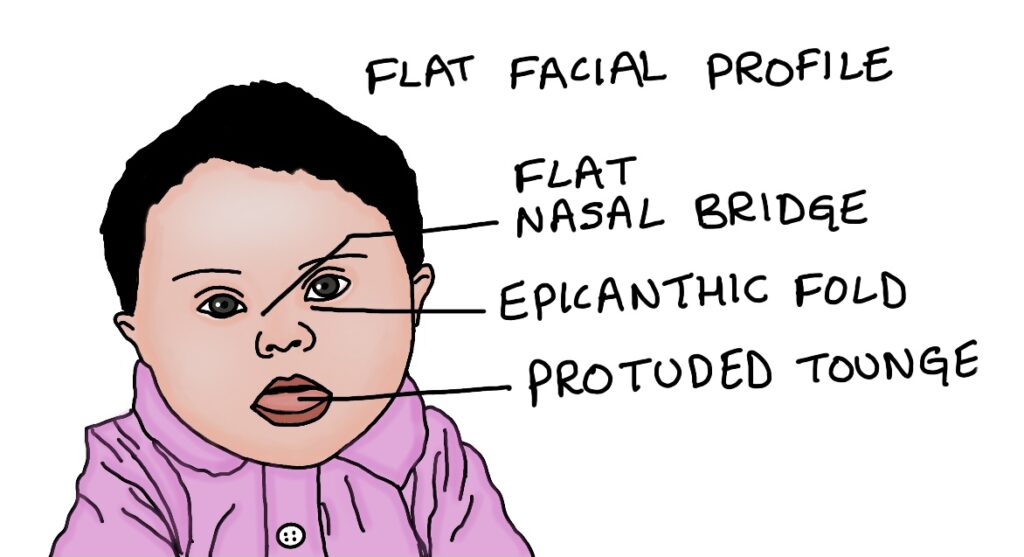
5.Epicanthic folds, flat nasal bridge and flat facial profile
6.Umbilical hernia
7.Hypotonia
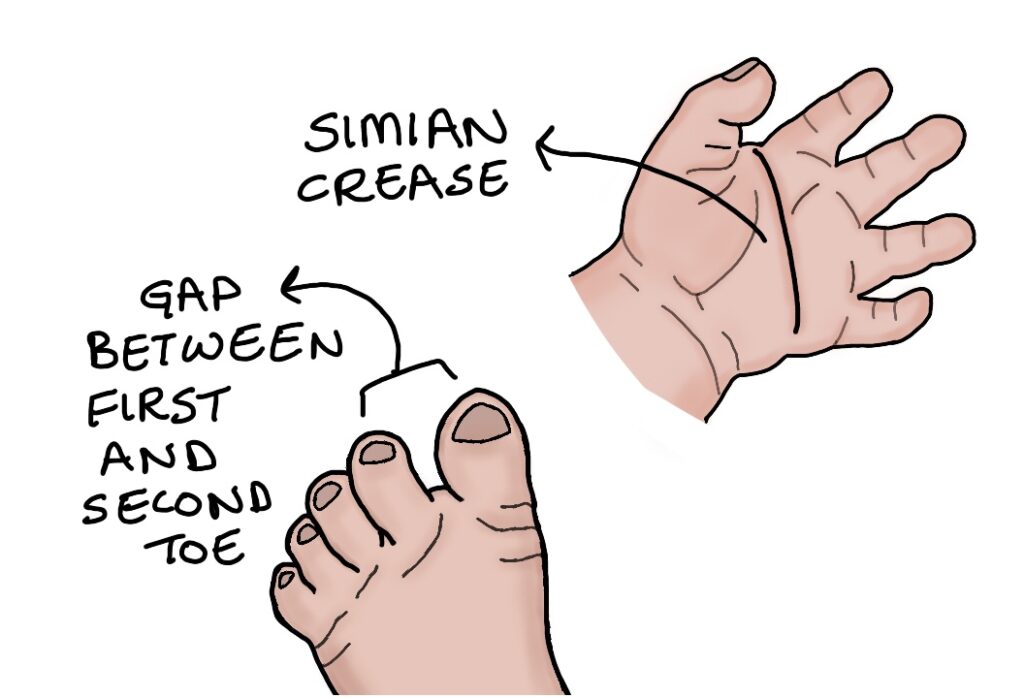
8.Gap between first and second toe
9.Tongue is protruding out of the mouth as the palate is narrow and the oral cavity cannot accommodate the tongue
10.A single prominent palmar crease Simian crease