It is the type of macrocytic anemia that is caused due to deficiency of vitamin B12 or folic acid. It is characterized by nuclear cytoplasmic asynchrony, where nuclear maturation lags behind cytoplasmic maturation.
Vitamin B12:
Vitamin B12 also known as Cobalamin is present in animal products like fish, milk, eggs and meat. Vegetarian food is deficient in vitamin B12.
1. Vitamin B12 is injected in a protein bound form.
2. In the stomach it gets detached from the binding protein through the action of pepsin and binds to a protein released from the salivary glands called haptocorrin.
3.In the duodenum, this bound vitamin B12 is released due to the action of pancreatic proteases and it now binds with intrinsic factor, which is released from the parietal cells of the stomach.
4. This vitamin B12- Intrinsic factor complex binds to cubulin receptors in the terminal ileum and gets absorbed.
5. After absorption, vitamin B12 binds to a transport protein called transcobalamin-II and is transported to perform various functions.
Deficiency occurs in vegetarians, infection with Diphyllobothrium Latum also known as fish tapeworm, malabsorption, pernicious anemia. Pernicious anaemia is an autoimmune disorder in which antibodies are produced against the parietal cells causing intrinsic factor deficiency.
Vitamin B12 gets converted to methyl cobalamin by the enzyme methyl transferase.This methyl cobalamin converts homocysteine to methionine in the presence of methyl transferase enzymes. In vitamin B12 deficiency, this step is impaired and homocysteine levels increase. Homocysteine damages the endothelial cells and results in atheroma formation, leading to increased risk of atherosclerosis. Methionine on the other hand is essential for the synthesis of choline which is involved in myelination. So, in vitamin B12 deficiency the decreased methionine levels also decrease choline causing impaired myelination.
Metabolism of odd chain fatty acids results in the formation of propionyl coA, which then converts into methyl malonyol coA. Methyl malonyol coA, in the presence of adenosyl cobalamin gets converted to succinyl coA by methyl malonyol coA mutase enzyme.Propionyl coA and methyl methylmalonyl coA accumulate in vitamin B12 deficiency. The accumulation and incorporation of propionyl coA into myelin sheets leads to demyelination of neurons.
Folic acid:
Folic acid is present in green leafy vegetables, citrus fruits and gets destroyed by cooking. Folic acid is present as polyglutamates in nature. In the jejunum due to the action of conjugase enzymes, these polyglutamates are broken down into di and mono glutamates. Its circulating form is methyl tetrahydrofolate.
Deficiency is mainly seen in alcoholics. Folic acid deficiency in pregnancy causes neural tube defects.
The methyl tetrahydrofolate gets converted to tetrahydrofolate by the enzyme methyl transferase.As discussed this is the same reaction forming methyl cobalamin. To recap, methyl tetrahydrofolate donates methyl group to vitamin B12 making it methylcobalamin while it becomes tetrahydrofolate. So in case of vitamin B12 deficiency, methyl tetrahydrofolate cannot be demylinated and cannot perform biochemical functions. This tetrahydrofolate is required for the conversion of serine into glycerine and get itself converted into methylene tetrahydrofolate. Methylene tetrahydrofolate inturn converts dUMP to dTMP and becomes dihydrofolate(DHF). Dihydrofolate reductase enzyme converts it back to tetrahydrofolate(THF). We know that dTMP that is, deoxythymidine monophosphate is needed for DNA synthesis. So of there is folic acid deficiency, dUMP cannot be converted into dTMP and DNA replication is impaired. But RNA synthesis is not impaired as it doesnot require dTMP.
Clinical features:
Fatigue, palour, hyperpigmentation of knuckles and atrophic glossitis can be seen. Atrophic glossitis is characterized by smooth, shiny, beefy red tongue.
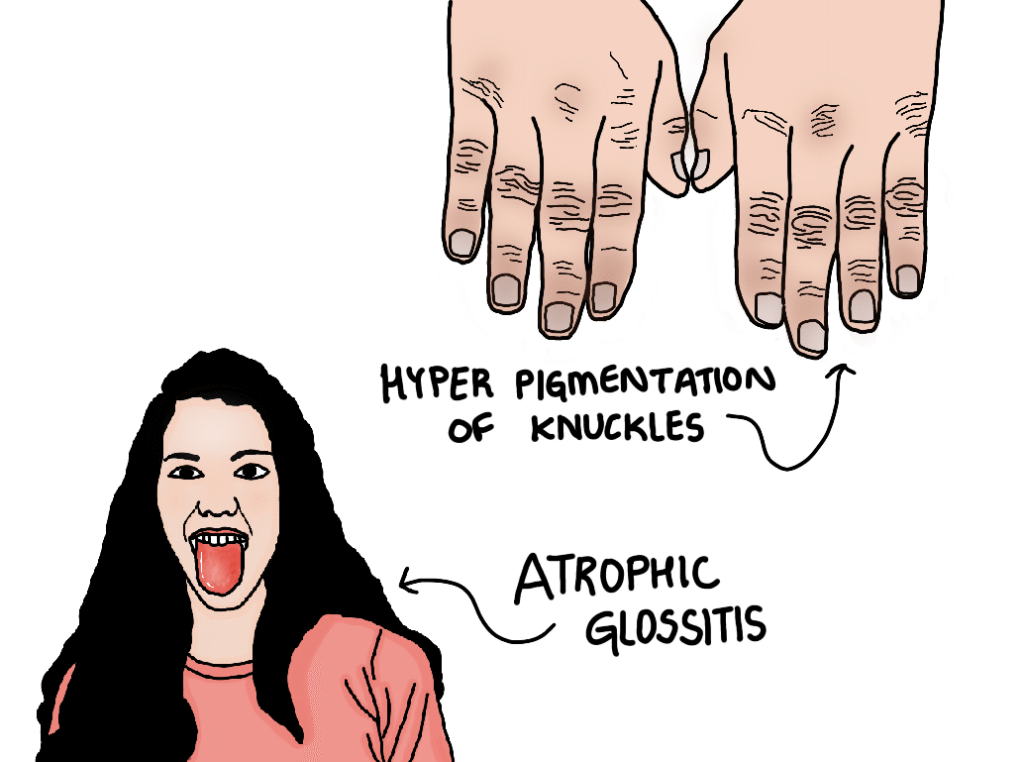
The clinical features are same in vitamin B12 and folic acid deficiency accept the neurological symptoms which are seen only in vitamin B12 deficiency. These neurological symptoms include sub acute combined degeneration of spinal cord, peripheral neuropathy, parasthesia which refers to abnormal sensations like pins and needles or tingling is seen due to demylination of sensory pathway neurons.
RBC indices:
Hemoglobin is reduced, MCV and MCH are increased while MCHC is normal.
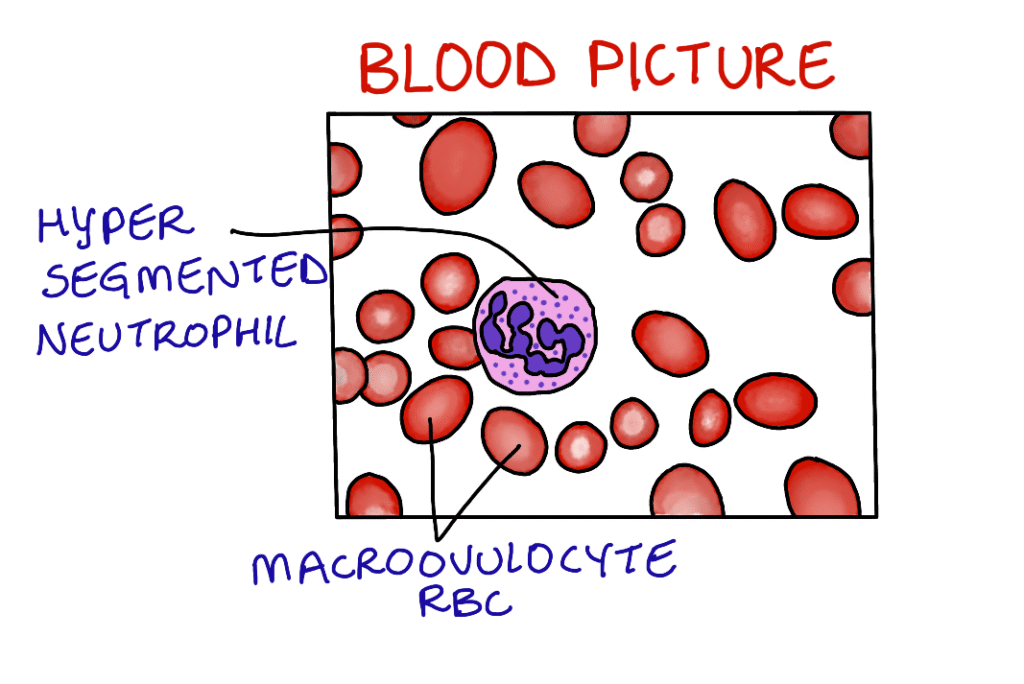
Blood and bone marrow picture:
Blood picture shows pancytopenia. Macroovulocyte RBCs and hyper segmented neutrophils are same. Bone marrow is hypercellular.
Biochemical findings:
Vitamin B12 and folic acid levels decrease, serum bilirubin, serum LDH increase and homocysteine, methyl malonyol coA levels also increase. Shilling test can be performed to know the cause of vitamin B12 deficiency and figlu test is used to access folic acid deficiency.
Treatment:
Based on the cause of megaloblastic anaemia, vitamin B12 injections or oral folic acid supplements are given.